06-原型模式
原型模式
原型(Prototype)模式指用一个已经创建的实例作为原型,通过复制该对象来创建一个和对象相同的或者相似的新对象。
由于无须关心对象具体创建的细节,所以原型模式创建对象非常高效。
模式的结构与实现
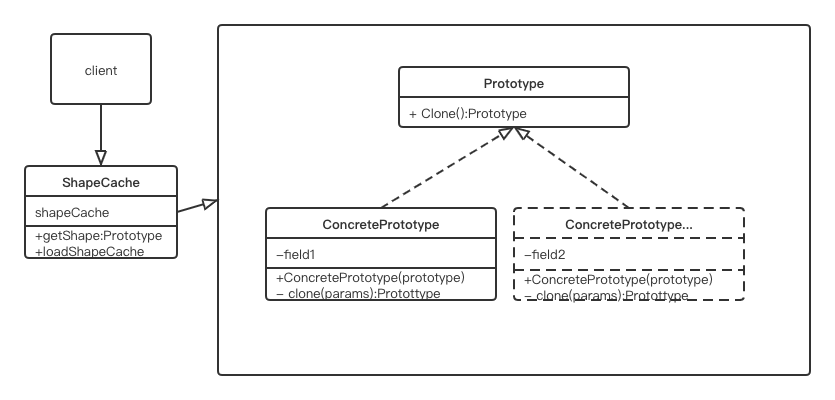
原型模式的主要角色:
- 抽象原型类:规定了具体原型对象必须实现的接口。
- 具体原型类:实现抽象原型类的clone()方法,它是可被复制的对象。
- 访问类:使用具体原型类中的clone()方法来复制新对象。
UML类图
实例
需求:创建一个抽象类Shape和扩展了Shape类的实体类。下一步是定义类ShapeCache,该类把shape对象存储在一个HashMap中,并在请求的时候返回它们的克隆。
实现代码步骤如下:
- 抽象原型类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34public abstract class Shape implements Cloneable {
private String id;
protected String type;
abstract void draw();
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(String type) {
this.type = type;
}
@Override
protected Object clone() {
Object o = null;
try {
o = super.clone();
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return o;
}
} - 具体原型类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32public class Circle extends Shape {
public Circle() {
super.type = "Circle";
}
@Override
void draw() {
System.out.println("圆圈");
}
}
public class Rectangle extends Shape {
public Rectangle() {
super.type = "Rectangle";
}
@Override
void draw() {
System.out.println("长方形");
}
}
public class Square extends Shape {
public Square() {
super.type = "Square";
}
@Override
void draw() {
System.out.println("正方形");
}
} - 创建访问类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21public class ShapeCache {
private static HashMap<String, Shape> shapeCache = new HashMap<>();
public static Shape getShape(String id){
Shape shape = shapeCache.get(id);
return (Shape) shape.clone();
}
public static void loadShapeCache() {
Circle circle = new Circle();
circle.setId("1");
shapeCache.put(circle.getId(), circle);
Square square = new Square();
square.setId("2");
shapeCache.put(square.getId(), square);
Rectangle rectangle = new Rectangle();
rectangle.setId("3");
shapeCache.put(rectangle.getId(), rectangle);
}
} - client根据ShapeCache来进行对象克隆
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ShapeCache.loadShapeCache();
Shape shape1 = ShapeCache.getShape("1");
shape1.draw();
Shape shape2 = ShapeCache.getShape("2");
shape2.draw();
Shape shape3 = ShapeCache.getShape("3");
shape3.draw();
}
} - 结果输出
1 | |
总结
优点
- 性能提高。
- 更方便的生成复杂对象。
缺点
- 必须实现Cloneable接口。
- 需要为每个类配置clone方法。
应用场景
- 需要复制一些对象。
- 资源优化(类初始化需要消化非常多的资源)。
本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-SA 4.0 协议 ,转载请注明出处!